knowledge-base
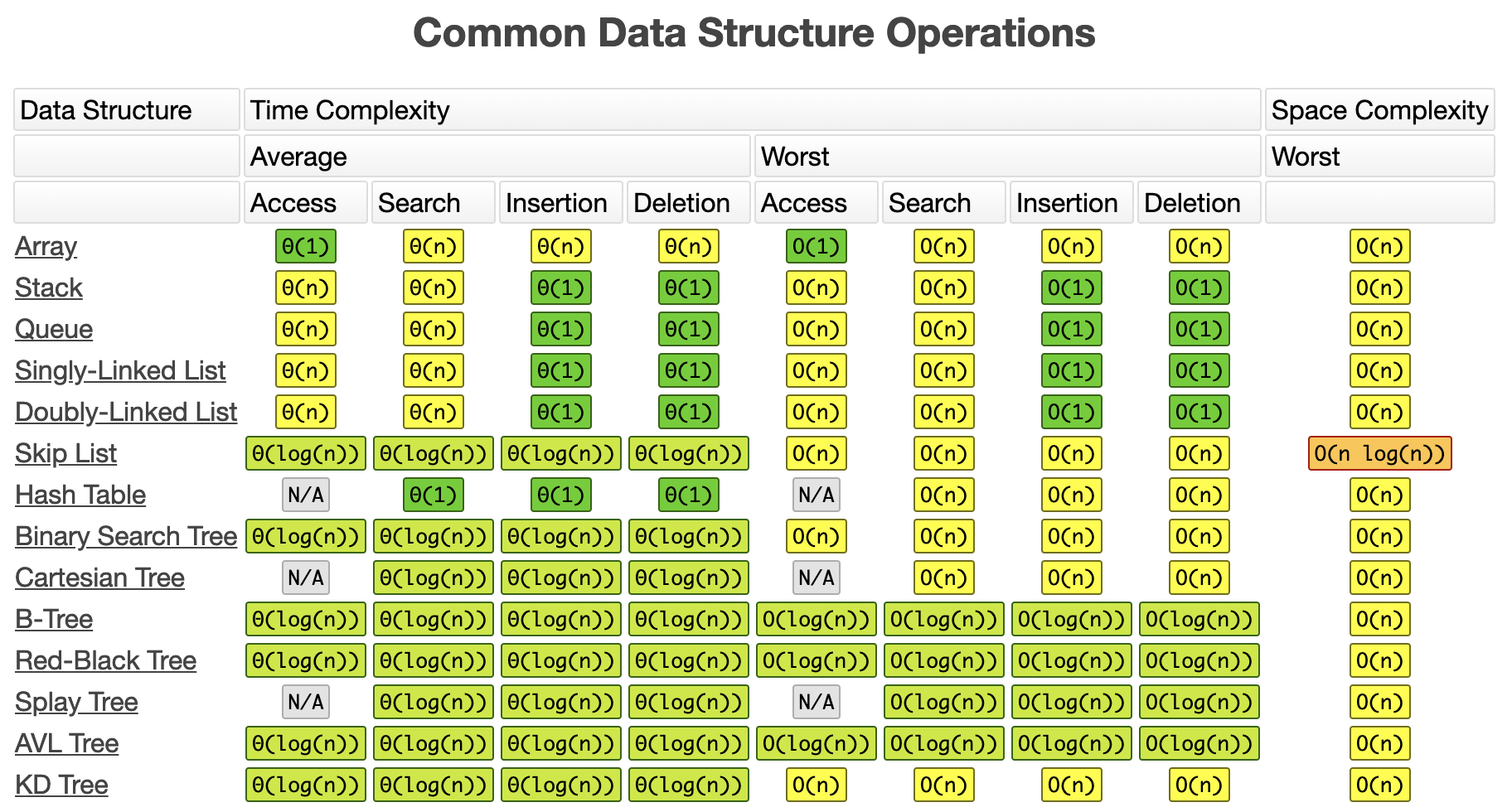
Binary Tree
- Part of the node based structures group
- We have again nodes, each node can have 3 elements, the first is a pointer to another node, the second is the value of the node and the thirs is also a pointer to another node.
- The node that is not referenced by any other node but refernces to other nodes is the root node.
- Follows the following rules
- Each node has either zero, one or two childeren
- If a node has two children, it must have one child that has a lesser value than the parent and one child that has a greater value than the parent.
-
Note that trees can be unbalanced and balanced.
- Search and access is O(log N) due to the nature that startin from the root node we can immediatly can eleminate half of the data structure for searching. This happens to each new step, therefore a logaritmic efficiency.
- Insertion: We have to search trough the tree to then find where to insert a new node. Therefore O(log N)
- Deletion is O(N) as due to the deletion, we might have to doe also a lookup to fix the haning children.
- Algoritm for deletion.
- If the node being deleted has no children, simply delete it
- If the node being deleted has one child, delete it and plug the child into the spot where the deleted node was.
- If the node being deleted has two childeren, replace the deleted node with the successor node. The successor node is the child node whose value is the least of all values that are greater than the deleted node.
- If the successor node has a right child, after plugging the successor into the spot of the deleted node, take the right child of the successor node and turn it into the left child of the parent of the successort node.
- Algoritm for deletion.